Because of the presence of hydrogen bonding - O - H - type O - and - O - H - N, making chitin molecular has strong hydrogen bonding and the crystal structure, lead to the chitin insoluble in water and general organic solvents
But the chitosan after taking off the acetylation reaction, its free amino increased, the crystal structure damaged, only soluble in dilute acid solution, so the applications are limited to large extent. After chitosan degradation, the molecular chain becomes short, molecular mass decreased.
So that, in water solution, the movement of molecular chain becomes disordered, the hydration of free amino enhanced, and its solubility improved in water.
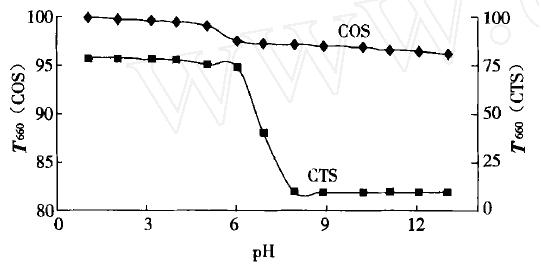
Figure 1: Oligochitosan's solubility under different pH environment.
As shown in chart, COS (short for oligochitosan) in pH value at 1 ~ 13 has good solubility in water, just when pH value is greater than 5.1, COS solubility in water began to fell slightly. But Chitosan (CTS) in pH value at 1 ~ 6 has good solubility in dilute acid, when pH value is greater than 6, it began to decline until almost insoluble. Therefore, low molecular of COS has good solubility in water, and high molecular chitosan has poor water solublity. In general, COS have good solubility in water, DP < 15
One of the most innovative approaches for controlling plant diseases is through the enhancement of the plant's own defence mechanisms (induced resistance), which would not involve the application of toxic compounds to plants. It has been well established for over 100 years, that plants can defend themselves; however, in the last 20 years, a significant progress in our knowledge on plant immunity, has provided the understanding required to allow induced resistance to be used in practice.
Chitosan oligosaccharide has been proven to be a plant elicitor which could induce plant defence responses. Firstly, Chitosan oligosaccharide is recognised by the receptor. After signal perception, the concentration ion flux alterations and reactive oxygens are changed. Theses changes trigger the signal transduction to regulate the expression of defence genes and change metabolism leading to plant resistance. The plants that have been preventively treated with chitooligosaccharides activate their defence mechanisms early, which leads to a faster and more effective response when the pathogen and environment stress try to colonise the plant.
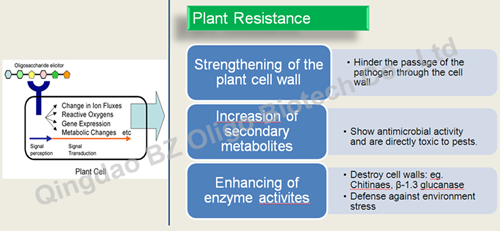
Chitooligosaccharide is a natural, non-toxic and biodegradable product, which does not leave any residues or affect the beneficial fauna. Chitooligosaccharide is a very useful tool for Integrated Pest Management (IPM), as it allows the reduction of the use of chemical plant protection products, thus contributing to a healthier and more sustainable agriculture. At the same time, chitooligosaccharide will facilitate plants' sale and, as a consequence, lead to higher profits.
Chitin and Chitosan had been approved beneficial for human body, and popular in medicine, nutrition, cosmetic, animal nutrition, agriculture and industry areas. Chitosan Oligosaccharide could be considered as water-soluble chitosan oligomer which is made from depolymerizing chitosan by enzyme. And its molecular weight (≤3kDa) is much lower than chitosan's (≥100KDa). The low molecular weight benefits prominent water solubility and bioactivities which have attracted the interest of many researchers and companies to utilize chitosan oligosaccharide for various applications.
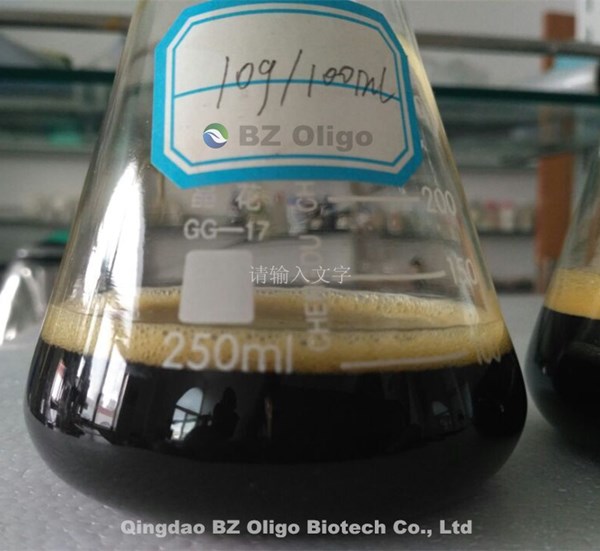

Figure 1: 10g chitosan oligosaccharides dissolve in 100ml water

Figure 2: 20g chitosan oligosaccharides dissolve in 100ml water

Figure 3: 30g chitosan oligosaccharides dissolve in 100ml water
10g, 20g & 30g of chitosan oligosaccharides completely dissolved in water by stirring 30 minutes at room temperature.

Figure 4: 10g chitosan oligosaccharides dissolve in 10ml water
While 10g chitosan oligosaccharides difficultly dissolved in 10ml water, and turned into a viscous "sludge".
So recommend to apply the chitosan oligosaccharide below 50% concentrations.
Chitosan oligosaccharide can replace the antibiotics, and can be used together with any medicine. It has stable chemical properties and can not react with any medicine. On the contrary, it can help improve the efficacy. Because of its special biological activities, it can reduce the side effects of medicines.
Some medicines have a negative influence on the liver of organism. In fact, chitosan oligosaccharide can directly have effect on the liver cell, relieve the load, alleviate the damage, and protect the liver.
Compared with other prebiotics, it works on different parts in the body, and plays different effects. And there is no antagonism between them.
|
|
Effects on microflora |
Stability |
Side -effect |
|||
|
oxygen |
gastric acid |
high temperature |
machining |
|||
|
Probiotics |
Promote growth of beneficial bacteria in the intestine, forming micro ecological competitive advantage |
Poor |
Poor |
Poor |
Poor |
Some strains may secrete antimicrobial |
|
Chitosan Oligosaccharide |
Promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, and inhibit the harmful bacteria |
Good |
Good |
Good |
Good |
None |
|
Antibiotics
|
Kill both harmful bacteria and beneficial bacteria |
Good |
Good |
Good |
Good |
Induce the animal endogenous infection or double infection, the generation of drug-resistant bacteria, the decline of immune function, and residues in animal products |
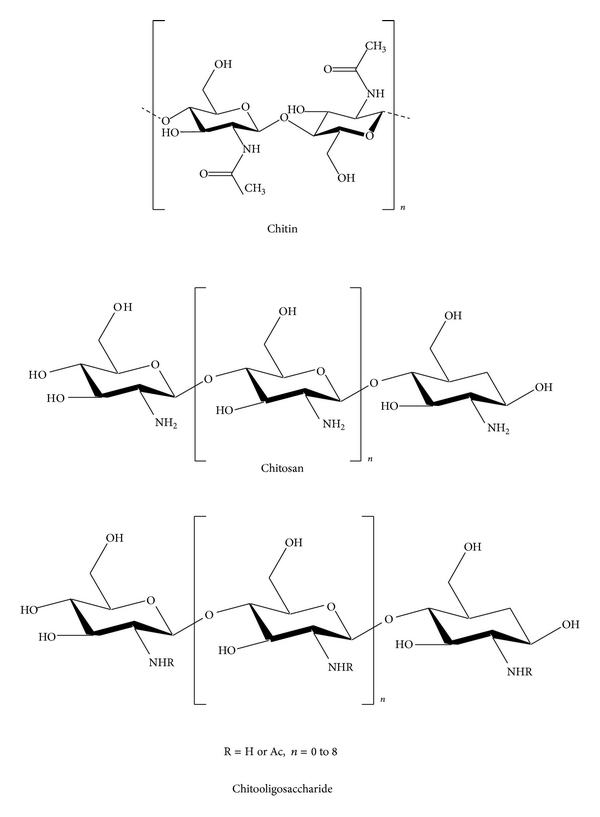
Chitin (Poly-N-acetyl-Glucosamine), is one of the second most abundant polymer after cellulose found in nature, present in the shells of all crustaceans and insects, and in certain other organisms including many fungi, algae, and yeast. The degree of acetylation (DA) is generally over 90%. It is chemically inert and highly insoluble in both water and acid.
The most important derivative of chitin is chitosan. Chitosan (Poly-D-Glucosamine), obtained by deacetylation of chitin which is removing the acetyl groups (CH3-CO-). The degree of acetylation is generally lower than 20%. Chitosan is insoluble in water, organic solvents, and aqueous bases and it is soluble after stirring in acids such as acetic, nitric, hydrochloric, perchloric, and phosphoric.
Compared to chitin, chitosan is relatively reactive. Because chitosan has been soluble in week acid and can be produced in various forms. Chitin and chitosan are known to have important functional activities, but poor solubility makes them difficult to use in various applications.
Chitooligosaccharides (Chitosan Oligomer), are the degraded products of chitosan by enzymatic hydrolysis, whose degrees of polymerization (DPs) are <20 and average molecular weight less than 3900Da.
Unlike chitosan, COS is readily soluble in water due to its shorter chain lengths and free amino groups in D-glucosamine units. The low viscosity and greater solubility of COS at neutral pH have attracted the interest of many researchers to utilize chitosan in its oligosaccharide form.

Definition:
Chitosan can only be dissolved in some dilute mineral acid or organic acid, not dissolve in the water directly, which limits its applications to large extent.
Water soluble chitosan can be classified into the following kind.
1. Chitosan that is soluble in water.
2. Chitosan Hydrochloride that is soluble in water
3. Carboxymethyl chitosan that is soluble in water
4. Low molecular chitin that is soluble in water.
5. Low molecular chitosan that is soluble in water.
These are regarded as water-soluble chitosan. Actually, only the first one is the true sense of water-soluble chitosan oligosaccharide that is dissolved in water. The ordinary chitosan is neither chitosan hydrochloride, nor carboxymethyl chitosan, nor low molecular material.
The way to decide the chitosan:
Put it in water, first see the solution viscosity, if no viscosity, it is low molecular chitin or low molecular chitosan. Second, add a few drops of NaOH solution in the aqueous solution, if producing precipitation, it is chitosan hydrochloride. If you add a few drops of HCl solution and it becomes turbidity, it is carboxymethyl chitosan, because carboxymethyl chitosan is actually a sodium carboxymethyl chitosan, if the solution is acidic, it is no longer a carboxylic acid sodium salt, but a carboxylic acid, and it is not soluble in acidic water.
The kinds of Water-soluble chitosan on the market:
1. Carboxymethyl chitosan (Expensive)
2. Chitosan Hydrochloride, chitosan quaternary ammonium salt, chitosan lactate salt, chitosan glutamate (Cheap)
3. Sulfated chitosan
4. Hyaluronic acid chitosan
5. Chitosan oligosaccharide
Water-soluble chitosan has the large molecular weight, soluble in water. And there is a large number of water soluble chitosan on the market which is not the true sense of water soluble chitosan.
